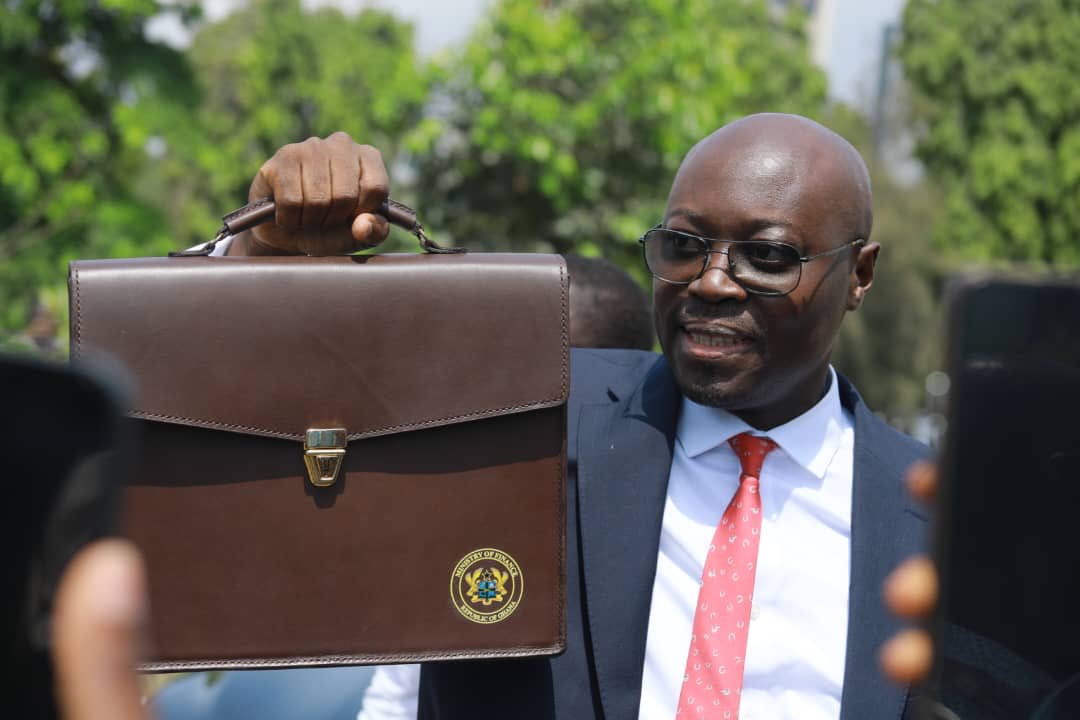
On 13 November 2025, Finance Minister Dr. Cassiel Ato Forson presented the 2026 Budget Statement and Economic Policy to Parliament.
According to DebrichGroup.com analyst, the budget arrives at a crucial moment as Ghana transitions from a period of economic stabilisation to a new phase of growth, job creation and structural transformation. Full Budget Text Here.
The overarching theme of the 2026 Budget is restoring economic stability while accelerating inclusive growth. With targeted investments, social protection, and improved fiscal discipline, the government hopes the upcoming year will strengthen the gains made in macroeconomic stability and unlock opportunities for millions of Ghanaians.
Main Highlights of the 2026 Budget
1. Stronger Economic Outlook for 2026
The government projects real GDP growth of around 5%, reflecting the country’s gradual recovery. Factors supporting this projection include:
-
Improved confidence in the Ghanaian economy
-
Stabilising inflation and exchange rate
-
Increased private-sector activity
-
Expected growth in agriculture and industry
-
Ongoing reforms in the energy and public sectors
2026 is positioned as the first full year of Ghana’s transition from stabilisation to economic expansion.
2. Fiscal Discipline and Debt Sustainability
A central element of the 2026 Budget is the government’s pledge to maintain fiscal discipline while achieving a primary surplus. Key strategies include:
-
Managing public debt through responsible borrowing
-
Strengthening expenditure controls
-
Improving arrears clearance to support private-sector liquidity
-
Enhancing transparency and predictability in public spending
The budget also outlines a medium-term path for further reducing the debt-to-GDP ratio between 2026 and 2029.
3. Revenue Mobilisation and Tax Measures
The government aims to boost domestic revenue without burdening low-income households. Major steps include:
-
Expanding the tax base through improved compliance
-
Strengthening revenue digitalisation
-
Enhancing collection of non-tax revenue and IGFs
-
Reviewing tax exemptions to eliminate abuse
-
Fine-tuning VAT administration for fairness and simplicity
A notable announcement is the removal of certain pandemic-era levies, easing pressure on businesses and consumers.
4. Prioritised Public Investment and Job Creation
Public investment will focus on sectors that create jobs and support long-term growth. Priority areas include:
a) Infrastructure Development
-
Major road construction and rehabilitation
-
Upgrading market infrastructure
-
Improvements in water and sanitation systems
-
Upgrades to transport and logistics networks
b) Energy and Power Generation
-
Construction of a new large-scale thermal power plant
-
Strengthening transmission infrastructure
-
Expanding renewable and alternative energy programmes
c) Agriculture and Food Security
-
Scaling up mechanisation, irrigation and extension services
-
Development of key agricultural value chains
-
Improving rural road networks to support market access
d) Industry and SME Support
-
Support for local manufacturers and industrial parks
-
Incentives for businesses to expand production
-
Job-oriented entrepreneurship and youth skills programmes
Government estimates indicate that up to 800,000 jobs will be created across the economy in 2026, especially in agriculture, construction, public works and small businesses.
5. Social Protection and Human Capital Development
The budget emphasises that fiscal consolidation will not come at the expense of the poor. Key social programmes receive renewed funding, including:
-
Livelihood Empowerment Against Poverty (LEAP)
-
School Feeding Programme
-
Support for persons with disabilities
-
Community-level nutrition and health programmes
-
Expanded youth employment and skills training
Government also plans to strengthen primary healthcare, maternal health services and disease-control initiatives.
Investment in education remains a priority, with improved funding for basic education, TVET expansion, digital skills training and tertiary-level infrastructure.
6. Public Sector and Governance Reforms
Improving public-sector efficiency is at the heart of the 2026 Budget. Major reforms include:
-
Broad digitalisation of public services
-
Enhanced procurement oversight
-
Stronger anti-corruption and accountability mechanisms
-
Performance-based budgeting
-
Better monitoring of state-owned enterprises
-
Improved payroll management
These reforms aim to ensure that every cedi of public funds delivers visible value to citizens.
7. Managing Risks and Safeguarding Growth
The budget identifies several risks that could affect implementation, including revenue shortfalls, global economic uncertainties and energy supply challenges. The government plans to:
-
Build fiscal buffers
-
Diversify exports and reduce reliance on imports
-
Strengthen financial-sector oversight
-
Maintain macroeconomic stability as the foundation of growth
These strategies are expected to cushion the economy and keep the country’s transformation agenda on track.
Medium-Term Outlook (2026–2029)
The medium-term framework shifts the economy toward transformation and investment-led growth. Between 2026 and 2029, government priorities will centre on:
-
Deepening industrialisation
-
Expanding agriculture and agro-processing
-
Growing the renewable energy sector
-
Enhancing digital infrastructure
-
Strengthening social protection
-
Maintaining a responsible fiscal path
This period is expected to consolidate Ghana’s journey towards a more resilient, diversified and inclusive economy.
Benefits of the 2026 Budget for Ghanaians
1. More Jobs and Economic Opportunities
The large-scale investment in infrastructure, agriculture and energy is expected to create hundreds of thousands of jobs and unlock opportunities for youth and entrepreneurs.
2. Stabilising Prices and Reducing Cost of Living
Continued macroeconomic stability—lower inflation, stable cedi, predictable government spending—helps reduce uncertainty for households and businesses.
3. Support for the Vulnerable
Improved funding for social protection programmes ensures that vulnerable communities are shielded from the effects of fiscal tightening.
4. Improved Infrastructure and Services
Better roads, markets, water systems and energy supply will improve living conditions and expand economic activity across the country.
5. Stronger Public Institutions
Reforms in procurement, digitalisation and public financial management improve transparency and public service delivery.
DOWNLOAD FULL BUDGET TEXT HERE